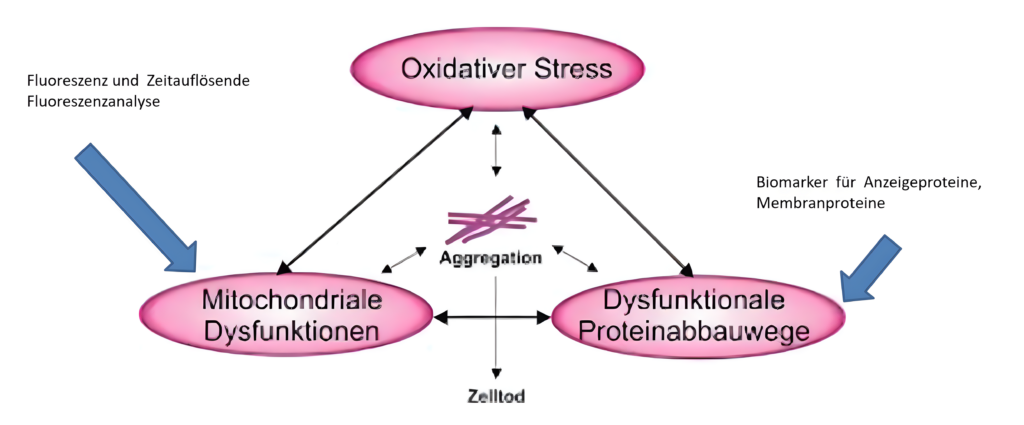
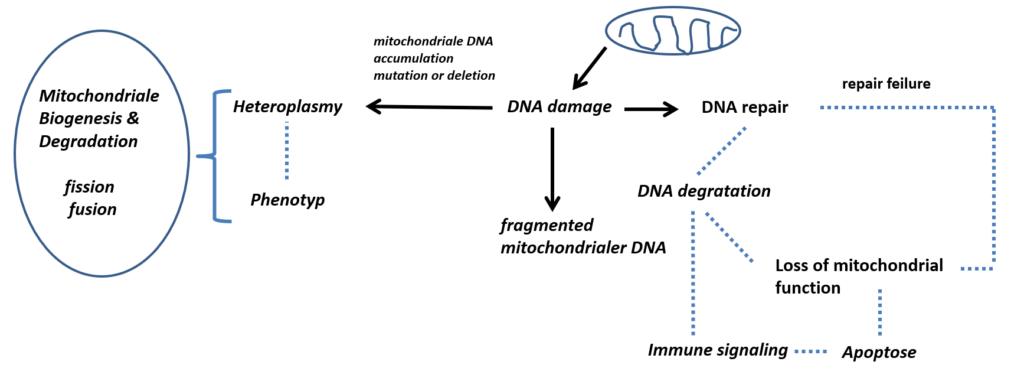
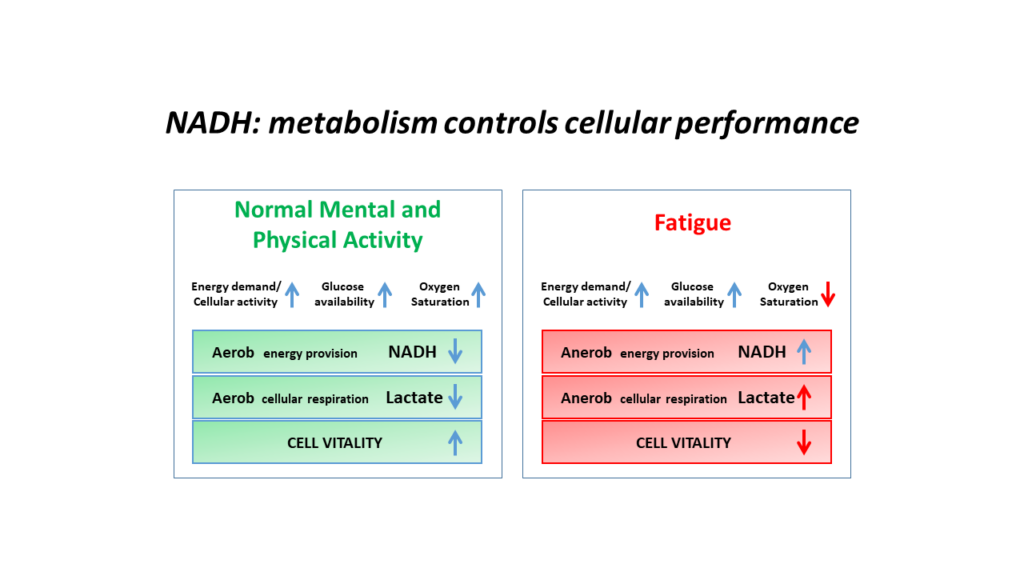
| Redoxsystem | Cytochrom C | Elektronen carrier | Diffusion bei Beschädigung der Mitochondrien in die äußere Membran und löst im Cytosol Apoptose aus | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder zeitauflösende Fluoreszenzmessung
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nicht invasiv |
| Redoxsystem | NADH | Elektronen carrier | Diffusion bei Beschädigung der Mitoschondrien in die äußere Membran | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nicht invasiv |
| Redoxsystem | OXPHOS | Synthese von ATP | ATP Transporter, ATP/ADP Translokale | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder zeitauflösende Fluoreszenzmessung
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nicht invasiv |
| Redoxsystem zellulärer Stressindikator | Mitofusin-2 oxydiertes Glutathion | - Regulation der mitochondrialen Fusion Veränderungen des intrazellulären Redoxzustandes
- Zentraler zellulärer Stressindikator | - | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder zeitauflösende Fluoreszenzmessung
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv |
| Redoxsystem | FAD | - Redoxpartner in der Atmungskette
- Elektronentransport | - | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv |
| anaerober Energiestoffwechsel | Laktatde-hydrogenase (LDH) | Bildung von L-laktat und NAD aus Pyruvat und NADH | Indikator für die Integrität der Zellmembran | Messmodus: größere Zeitintervalle
Messfrequenz: mittel
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Zeitauflösende Fluoreszenzmessung
Messort: lokal, nicht invasiv oder systemisch im Blut |
| ROS Abwehr | Superoxid-dismutase (SOD) | primäres enzymatisches Antioxydans | - | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv |
| ROS Abwehr | Gluthathion-peroxidase
| primäres enzymatisches Antioxydants | - | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
|
| ROS Abwehr | Gluthathion-reduktase | sekundäres enzymatisches Antioxydants
| - | Messmodus: permanent
Messfrequenz: hoch
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz
Messort: lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
|
| mitchondriale Stressabwehr | SIRT 3 | - NAD+ abhängige Decarboxylase
- Regulation der mitochondrialen Funktion nach metabolischen Stress
- Regulation der mitochondrialen Funktion nach metabolischen Stress
| - | Messmodus: Intervall
Messfrequenz: niedrig
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Biomarker
Messort:
- lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
- systemisch im Blut
|
| mitchondriale Stressabwehr | NRF 2 | - Transkriptionsfaktor
- Makroautophagie fehlehafter Proteine
- antiinflammatorisch
- Apoptose und mitochondriale Biogenese
- Reaktivität auf chemisch induzierten mitochondrialen Stress
- wichtige Rolle bei oxydativen Stress
| - | Messmodus: Intervall
Messfrequenz: niedrig
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Biomarker
Messort:
- lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
- systemisch im Blut
|
| Apoptoseregulation | BCL-2 und BCL-x | - Regulation der Apoptose durch Steuerung des transmembranale Cytochrom C Durchtritt
- Aufrechterhaltung der mitochondrialen Atmungskapazität
| - | Messmodus: Intervall
Messfrequenz: niedrig
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Biomarker
Messort:
- lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
- systemisch im Blut
|
| mitochondriale Reparation und Regeneration | Mitofusin-2 (MFN2) | - Regulation der mitochonsdrialen Fusion und Bioenergetik
- Veränderung des intrazellulären Redoxzustandes
- Induziert die mitochondriale Fusion
| - | Messmodus: Intervall
Messfrequenz: niedrig
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Biomarker
Messort:
- lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
- systemisch im Blut
|
| mitochondriale Regeneration | DRP1 | GTPase für die mitochondriale Spaltung
| - | Messmodus: Intervall
Messfrequenz: niedrig
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Biomarker
Messort:
- lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
- systemisch im Blut
|
| Redoxsystem | Carbonic anhydrase II | Lactat flux für die nicht katalytisch Laktatverarbeitung
| - | Messmodus: Intervall
Messfrequenz: niedrig
Messverfahren: Autofluoreszenz oder Biomarker
Messort:
- lokal, invasiv oder nichtinvasiv
- systemisch im Blut
|